Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tsubota, Yoichi; Porcheron, E.*; Journeau, C.*; Delacroix, J.*; Suteau, C.*; Lallot, Y.*; Bouland, A.*; Roulet, D.*; Mitsugi, Takeshi
Proceedings of International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM2023) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2023/10
In order to safely remove fuel debris from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), it is necessary to quantitatively evaluate radioactive airborne particulate generated by the cutting of nuclear fuel debris. We fabricated Uranium-bearing simulated fuel debris (SFD) with In/Ex-Vessel compositions and evaluated the physical and chemical properties of aerosols generated by heating the SFDs. Based on these results, we estimated the isotopic composition and radioactivity of aerosols produced when 1F-Unit2 fuel debris is laser cut, which is a typical example of a heating method. Plutonium, mainly  Pu,
Pu, Am, and
Am, and  Cm were found to be the alpha nuclide, and
Cm were found to be the alpha nuclide, and  Pu,
Pu,  Cs-Ba, and
Cs-Ba, and  Sr-Y were found to be the beta nuclide of interest.
Sr-Y were found to be the beta nuclide of interest.
Porcheron, E.*; Journeau, C.*; Delacroix, J.*; Berlemont, R.*; Bouland, A.*; Lallot, Y.*; Tsubota, Yoichi; Ikeda, Atsushi; Mitsugi, Takeshi
Proceedings of International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM2023) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2023/10
Results of the URASOL project aimed at evaluating the generation and dispersion of radioactive aerosols during the cutting of fuel debris, a key issue in the decommissioning of the damaged reactors at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), are presented in this report. Characterization of aerosols generated during heating and mechanical cutting of simulated fuel debris in terms of mass concentration, real-time number density, mass-based particle size distribution, morphology, and chemical properties is reported. In the heating tests, an increase in particle size with increasing temperature was observed, and in terms of particle number density, the case using depleted uranium simulated fuel debris had a smaller number density than the test using Hf-containing simulated fuel debris. In mechanical cleavage, the aerodynamic median mass diameter of the aerosol was almost the same for the radioactive and non-radioactive samples (about 3.7 4.4
4.4  m).
m).
Shimada, Taro; Sasagawa, Tsuyoshi; Miwa, Kazuji; Takai, Shizuka; Takeda, Seiji
Proceedings of International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM2023) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2023/10
Nuclear regulatory inspection should be performed on the basis of the risk information during the decommissioning phase of the nuclear power plant. However, it is difficult because the methodology for quantitatively assessing the radiation exposure risk during decommissioning activities has not been established. Therefore, a decommissioning risk assessment code, DecAssess-R, has been developed based on the decommissioning safety assessment code, DecAssess, which creates event trees from initiating events and evaluates the radiation risk resulting from public exposure dose for each accident sequence. The assessment took into account that mobile radioactive inventories that can be easily dispersed in the work area, such as radioactive dust accumulated in HEPA filters attached to a contamination control enclosure, will fluctuate with the progress of the decommissioning work. Initiating events were selected based on the investigation of accidents and malfunctions during dismantling, disassembly, and component replacement activities around the world, and event trees were created from the initiating events to indicate the progress scenario. The frequencies of occurrence were determined with reference to general industry data in addition to the above accidents and malfunctions, and the probabilities of event progression were determined with reference to failure data during the operation phase. The exposure risks during dismantling of components in the reference BWR were evaluated. As a result, the public exposure dose was maximum in case of fire during dismantling of reactor internals and fire spread to combustibles and filters, including radioactivity temporarily stored in the work area. The exposure risk was also maximum because the probability of occurrence of this accident sequence was greater than that of other scenarios.
Kanzaki, Norie; Sakoda, Akihiro; Kataoka, Takahiro*; Sun, L.*; Tanaka, Hiroshi; Otsu, Iwao*; Yamaoka, Kiyonori*
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(17), p.10750_1 - 10750_14, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Environmental Sciences)Reactive sulfur species (RSS) involve oxidative stress deeply and contribute anti-inflammatory effect, but no studied have focused on RSS changes after irradiation. In this study, we comprehensively analyzed the metabolites, focusing on RSS in mouse brain following radon inhalation. The ratio of oxidized glutathione to reduced glutathione and proportion of RSS in GSH or cysteine increased by radon inhalation. The sulfur ion might bind to GSH or cysteine chemically under conditions of oxidative stress, even at very low-dose exposure. We performed the overall assessment of high-dimensional data by applying machine learning and showed the specific characteristics of the effects by the exposure conditions. Our results suggested that RSS could produce a biological defense against oxidative stress following radon inhalation.
 Be activity concentrations in the atmosphere
Be activity concentrations in the atmosphereNarazaki, Yukinori*; Sakoda, Akihiro; Akata, Naofumi*; Ito, Hisanori*; Momoshima, Noriyuki*
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(16), p.10128_1 - 10128_9, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:27.46(Environmental Sciences)In March 2013, increased  Be activity concentrations in the atmosphere were observed for successive days in Dazaifu, western Japan. The daily
Be activity concentrations in the atmosphere were observed for successive days in Dazaifu, western Japan. The daily  Be activity concentration averages ranged from 0.93 to 14 mBq/m
Be activity concentration averages ranged from 0.93 to 14 mBq/m , with a monthly average of 8.3 mBq/m
, with a monthly average of 8.3 mBq/m . This average was the highest among the monthly averages observed between 1999 and 2015 and higher than the monthly average over this period (4.7 mBq/m
. This average was the highest among the monthly averages observed between 1999 and 2015 and higher than the monthly average over this period (4.7 mBq/m ) plus twice the standard deviation (1.7
) plus twice the standard deviation (1.7  2 mBq/m
2 mBq/m = 8.1 mBq/m
= 8.1 mBq/m ). Also, this exceeded the monthly average (6.0 mBq/m
). Also, this exceeded the monthly average (6.0 mBq/m ) only for March 1999-2015, excluding 2013, where the cosmic-ray intensity, a component producing
) only for March 1999-2015, excluding 2013, where the cosmic-ray intensity, a component producing  Be, decreased. Based on the backward trajectory analysis results, the inflow of air from the stratosphere and upper troposphere at high latitudes that frequently occurred in March 2013 was considered the reason for the
Be, decreased. Based on the backward trajectory analysis results, the inflow of air from the stratosphere and upper troposphere at high latitudes that frequently occurred in March 2013 was considered the reason for the  Be activity concentration increase.
Be activity concentration increase.
Sakoda, Akihiro; Ishida, Tsuyoshi*; Kanzaki, Norie; Tanaka, Hiroshi; Kataoka, Takahiro*; Mitsunobu, Fumihiro*; Yamaoka, Kiyonori*
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(13), p.7761_1 - 7761_12, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Environmental Sciences)In specific situations such as bathing in a radon spa, where the radon activity concentration in thermal water is far higher than that in air, it has been revealed that radon uptake via skin can occur and should be considered for more precise dose evaluation. The primary aim of the present study was to numerically demonstrate the distribution as well as the degree of diffusion of radon in the skin, with a focus on its surface layers (i.e., stratum corneum). We made a biokinetic model that included diffusion theory at the stratum corneum, and measured radon solubility in the stratum corneum to get a crucial parameter. The implementation of the model suggested that the diffusion coefficient in the stratum corneum was as low as general radon-proof sheets. The depth profile of radon in the skin was found to be that after a 20-minute immersion in water, the radon activity concentration at the top surface skin layer was approximately 1000 times higher than that at the viable skin layer. The information on the position of radon as a radiation source would contribute to special dose evaluation where specific target cell layers are assumed for the skin.
Ogura, Koya*; Hosoda, Masahiro*; Tamakuma, Yuki*; Suzuki, Takahito*; Yamada, Ryohei; Negemi, Ryoju*; Tsujiguchi, Takakiyo*; Yamaguchi, Masaru*; Shiroma, Yoshitaka*; Iwaoka, Kazuki*; et al.
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(3), p.978_1 - 978_16, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:68.83(Environmental Sciences)Kasahara, Shigeki; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Hata, Kuniki; Fukuya, Koji*; Fujii, Katsuhiko*
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems - Water Reactors (Internet), p.1345 - 1355, 2019/08
This paper describes empirical equation development of crack growth rates (CGR) in consideration of IASCC of neutron irradiated stainless steel to contribute to structural integrity assessment of BWR reactor internals. Empirical equations of CGR (da/dt) were developed based on a formula of da/dt = M K
K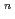 , assuming that "M" and "n" tend to be saturated with increasing neutron fluence. To obtain the empirical equations for normal water chemistry (NWC) and hydrogen water chemistry (HWC) of BWR, a data fitting with least square method was applied to the datasets consisting of F, K and CGR from post irradiation examinations of neutron irradiated stainless steel under simulated NWC and HWC conditions from open literature. As a result, calculated results by the equation for NWC showed good agreement with measured CGR data, meanwhile those for HWC did not. The above difference was seemed to be attributed that CGR data obtained under HWC conditions were scattered extensively.
, assuming that "M" and "n" tend to be saturated with increasing neutron fluence. To obtain the empirical equations for normal water chemistry (NWC) and hydrogen water chemistry (HWC) of BWR, a data fitting with least square method was applied to the datasets consisting of F, K and CGR from post irradiation examinations of neutron irradiated stainless steel under simulated NWC and HWC conditions from open literature. As a result, calculated results by the equation for NWC showed good agreement with measured CGR data, meanwhile those for HWC did not. The above difference was seemed to be attributed that CGR data obtained under HWC conditions were scattered extensively.
Fukuya, Koji*; Fujii, Katsuhiko*; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Hata, Kuniki
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems - Water Reactors (Internet), p.523 - 531, 2019/08
For structural integrity assessment on reactor internals of light water reactors, empirical equations of tensile properties as a function of neutron dose, and trend curves of stress-strain relations of neutron-irradiated austenitic stainless steels was proposed by fitting to recently developed database. The data in the database were obtained from reports of national projects in Japan and open literature, which was summarized in the form of data sheets. The empirical equations for tensile properties were formulated by using a saturation-type formulae. The equations were for CW 316 and SA 304/316 stainless steels in the temperature range of 280-350 C and the dose range up to 80 dpa. Stress-strain relation curves were reproduced based on the Swift model. Obtained calculated results by the empirical equations and stress-strain relations were reasonably well fitted to experimental data. The effects of composition and cold-working, etc. on tensile properties were discussed.
C and the dose range up to 80 dpa. Stress-strain relation curves were reproduced based on the Swift model. Obtained calculated results by the empirical equations and stress-strain relations were reasonably well fitted to experimental data. The effects of composition and cold-working, etc. on tensile properties were discussed.
Pratama, M. A.; Takahara, Shogo; Munakata, Masahiro; Yoneda, Minoru*
Environment International, 115, p.196 - 204, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:7.2(Environmental Sciences)Nakayama, Hiromasa; Takemi, Tetsuya*
International Journal of Environment and Pollution, 64(1/3), p.125 - 144, 2018/00
We have attempted to develop a practical and quick local-scale atmospheric dispersion calculation method using an overlapping technique for plume concentration distributions in an emergency response to nuclear accidents. In order to evaluate the overlapping approach, we performed LESs of turbulent flows and plume dispersion under varying mean wind directions using the meteorological data as the model input. When compared with the simulated results under the real meteorological condition, it is shown that the concentration distribution patterns are reasonably simulated by the overlapping method. It can be concluded that the atmospheric dispersion calculation method using the overlapping technique has potential performance for emergency responses to nuclear accidents.
Aoki, So; Kondo, Keietsu; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems - Water Reactors, Vol.2, p.663 - 672, 2018/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:58(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The objective of this study was to clarify effect of long-term thermal aging on SCC initiation susceptibility in low carbon austenitic stainless steels. Specimens used were Type 304L and 316L steels. Both steels were cold rolled to 20% thickness reduction (CW) and then followed by long-term thermal aging at 288 C for 14,000 h (LTA). Crevice Bent Beam (CBB) test was carried out to estimate the SCC initiation susceptibility under BWR simulated water condition at high temperature. The present results of the CBB tests showed that 304L CW + LTA exhibited no SCC susceptibility. In contrast, the SCC initiation susceptibility of 316L increased by the combination of cold rolling and long-term thermal aging. To understand these results, evaluation on the changes in microchemistry, microstructure and mechanical properties induced by the CW and LTA treatment has been developed, and their correlation with the SCC initiation susceptibility is discussed.
C for 14,000 h (LTA). Crevice Bent Beam (CBB) test was carried out to estimate the SCC initiation susceptibility under BWR simulated water condition at high temperature. The present results of the CBB tests showed that 304L CW + LTA exhibited no SCC susceptibility. In contrast, the SCC initiation susceptibility of 316L increased by the combination of cold rolling and long-term thermal aging. To understand these results, evaluation on the changes in microchemistry, microstructure and mechanical properties induced by the CW and LTA treatment has been developed, and their correlation with the SCC initiation susceptibility is discussed.
Soma, Yasutaka; Kato, Chiaki; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems - Water Reactors, Vol.2, p.509 - 521, 2018/00
In-situ electrochemical measurement within crevice of stainless steel in 288 C water has been conducted to analyze crevice water chemistry. Small sensors (
C water has been conducted to analyze crevice water chemistry. Small sensors (
 250
250 m) measured local solution electrical conductivity,
m) measured local solution electrical conductivity, 
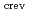 , polarization resistance, and electrochemical corrosion potential. Real-time response of the
, polarization resistance, and electrochemical corrosion potential. Real-time response of the 
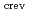 as functions of bulk water conductivity, dissolved oxygen (DO) concentration has been quantitatively analyzed. The effect of geometrical factors on the crevice environment was also studied. The
as functions of bulk water conductivity, dissolved oxygen (DO) concentration has been quantitatively analyzed. The effect of geometrical factors on the crevice environment was also studied. The 
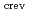 differ more than an order of magnitude depending on the oxygen potential inside the crevice. The
differ more than an order of magnitude depending on the oxygen potential inside the crevice. The 
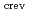 increased by small amount of bulk DO (e.g. 30 ppb). Maximum
increased by small amount of bulk DO (e.g. 30 ppb). Maximum 
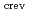 was observed with DO of 32000 ppb and became more than 100 times higher than that of bulk water. Crevice geometry affected significantly on the water chemistry inside.
was observed with DO of 32000 ppb and became more than 100 times higher than that of bulk water. Crevice geometry affected significantly on the water chemistry inside.
Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kasahara, Shigeki; Seto, Hitoshi*; Kitsunai, Yuji*; Koshiishi, Masato*; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems - Water Reactors, Vol.2, p.1039 - 1054, 2018/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:58(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)In order to understand irradiation-assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) growth behavior, crack growth rate (CGR) tests have been performed in simulated Boiling Water Reactor water conditions at  288
288 C on neutron-irradiated 316L stainless steels (SSs) at
C on neutron-irradiated 316L stainless steels (SSs) at  12-14 dpa. After the tests, the microstructures near the crack tip of the specimens are examined with scanning transmission electron microscope (FE-STEM). In comparison with a previous study at
12-14 dpa. After the tests, the microstructures near the crack tip of the specimens are examined with scanning transmission electron microscope (FE-STEM). In comparison with a previous study at 
 2 dpa, this result shows a less benefit of low electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP) conditions on CGR. A crack tip immersed over 1000 hours was filled with oxides, while almost no oxide film was observed near the crack front in the low-ECP conditions. In addition, a high density of deformation twins and dislocations were found near the fracture surface of the crack front. It is considered that both localized deformation and oxidation are possible dominant factors for the SCC growth in highly irradiated SSs.
2 dpa, this result shows a less benefit of low electrochemical corrosion potential (ECP) conditions on CGR. A crack tip immersed over 1000 hours was filled with oxides, while almost no oxide film was observed near the crack front in the low-ECP conditions. In addition, a high density of deformation twins and dislocations were found near the fracture surface of the crack front. It is considered that both localized deformation and oxidation are possible dominant factors for the SCC growth in highly irradiated SSs.
 -ray spectra obtained via aerial radiation monitoring using an unmanned helicopter
-ray spectra obtained via aerial radiation monitoring using an unmanned helicopterOchi, Kotaro; Sasaki, Miyuki; Ishida, Mutsushi*; Hamamoto, Shoichiro*; Nishimura, Taku*; Sanada, Yukihisa
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(8), p.926_1 - 926_14, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:22.71(Environmental Sciences)After the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, the vertical distribution of radiocesium in soil has been investigated to better understand the behavior of radiocesium in the environment. The typical method used for measuring the vertical distribution of radiocesium is troublesome because it requires collection and measurement of the activity of soil samples. In this study, we established a method of estimating the vertical distribution of radiocesium by focusing on the characteristics of  -ray spectra obtained via aerial radiation monitoring using an unmanned helicopter. In this method, the change in the ratio of direct
-ray spectra obtained via aerial radiation monitoring using an unmanned helicopter. In this method, the change in the ratio of direct  rays to scattered
rays to scattered  rays at various depths in the soil was utilized to quantify the vertical distribution of radiocesium. The results show a positive correlation between the abovementioned and the actual vertical distributions of radiocesium measured in the soil samples.
rays at various depths in the soil was utilized to quantify the vertical distribution of radiocesium. The results show a positive correlation between the abovementioned and the actual vertical distributions of radiocesium measured in the soil samples.
Yamaguchi, Masatake; Ebihara, Kenichi; Itakura, Mitsuhiro
Proceedings of 2016 International Hydrogen Conference (IHC 2016); Materials Performance in Hydrogen Environments, p.563 - 571, 2017/00
no abstracts in English
Ebihara, Kenichi; Saito, Kei*; Takai, Kenichi*
Proceedings of 2016 International Hydrogen Conference (IHC 2016); Materials Performance in Hydrogen Environments, p.470 - 477, 2017/00
For understanding hydrogen (H) embrittlement of steels, it is necessary to infer the state that defects trap H in the steels. Thermal desorption spectra of H obtained by the thermal desorption spectrometry (TDS) are used for inferring such a state. Because the thermal desorption spectra include the influence of experimental conditions and hydrogen diffusion as well as information of the defects trapping H, it is necessary to interpret the spectra using the numerical simulation. In the presentation, we determined the detrapping and the trapping rate constants which are necessary for the simulation from the experimental spectra obtained for plate specimens which is so small that H diffusion is ignorable. Then we confirmed that the model using the obtained rate constants can simulate the spectra of larger cylindrical specimens, so that it was found that the rate constant for small specimens can be used for the simulation of the spectra for specimens of different shape or size.
Kato, Chiaki; Sato, Tomonori; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Yamagishi, Isao
Proceedings of 17th International Conference on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems - Water Reactors, Vol.2, p.1357 - 1374, 2016/05
With respect to the long-term storage of the zeolite-containing spent Cs adsorption vessels used at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, the corrosion of the vessel material is one of the most important issues. In this study, we performed electrochemical tests on stainless steel specimens in zeolite-containing artificial seawater under gamma-ray irradiation. The spontaneous potential ESP and critical pitting potential VC of the type 316L steel in systems in contact with various zeolites were measured in order to evaluate the corrosion resistance of the steel. In addition, the water sample was analyzed after being irradiated, in order to determine the concentrations of various dissolved oxidants such as oxygen and hydrogen peroxide, which can accelerate the corrosion process. The steady-state rest potential increased with an increase in the dose rate; however, the increase was suppressed in contact with the zeolites. The VC value of the steel when in contact with the zeolites was slightly smaller than the VC value in bulk water; however, the choice of the zeolite used as herschelite, IE96 and IE911 hardly affect the VC value. The concentration of H O
O in the bulk water under irradiation also increased with the increase in the dose rate. This increase was suppressed in the systems in contact with the zeolites, owing to the decomposition of the H
in the bulk water under irradiation also increased with the increase in the dose rate. This increase was suppressed in the systems in contact with the zeolites, owing to the decomposition of the H O
O by the zeolites. A clear relationship was observed between ESP and the H
by the zeolites. A clear relationship was observed between ESP and the H O
O concentration. As contact with the zeolites caused the increase in ESP under irradiation to be suppressed, it can be concluded that the presence of zeolites in the spent Cs adsorption vessels can reduce the probability of the localized corrosion of the stainless steel in the vessels.
concentration. As contact with the zeolites caused the increase in ESP under irradiation to be suppressed, it can be concluded that the presence of zeolites in the spent Cs adsorption vessels can reduce the probability of the localized corrosion of the stainless steel in the vessels.
Sasao, Eiji; Yuguchi, Takashi*; Ito, Yasuto*; Inoue, Takashi*; Ishibashi, Masayuki
Proceedings of 10th Asian Regional Conference of International Association for Engineering Geology and the Environment (IAEG ARS 2015) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2015/09
Understanding of the fracture network is important for disposal of high-level radioactive waste. We present our hypothesis on the formative mechanism of inhomogeneous distribution of fracture in the Toki Granite. In the Toki Granite, low- and high-angle fractures are abundant at the shallower part, while less at the deeper part where high-angle fracture is dominant. Distribution of the high-angle fracture is inhomogeneous. Thermochronological study revealed that the rapid cooling occurred at the early stage of granite formation. Paleomagnetic directions of the intact granite were dispersed. This suggests granite was plastically deformed during rapid cooling period. The rapid cooling might cause inhomogeneous distribution of cooling strain. When the granite reached to brittle deformation field, inhomogeneous fracture distribution was formed by the inhomogeneous strain. If so, recognition of the cooling history is essential to understand the distribution of the fracture network.
Ishii, Eiichi; Hashimoto, Yuta; Inagaki, Daisuke*
Proceedings of 10th Asian Regional Conference of International Association for Engineering Geology and the Environment (IAEG ARS 2015) (USB Flash Drive), 4 Pages, 2015/09
This manuscript describes unpredicted inflow which occurred during tunnel excavation for a permeable fault zone with clay-rich gouge although the fault zone was pregrouted. Some observational evidence indicates that the gouge was increasingly washed out into the tunnel through the rockbolts penetrating the gouge and the boundary between the shotcrete and the gouge on the excavation side wall during excavation. The resultant piping/erosion of the gouge probably accelerated groundwater flow from the outer aquifer of the pregrouted zone to the tunnel. After an excavation outcrop exposing the fault zone was temporarily shotcreted, major inflow occurred from the nucleated flow channel in the fault zone, breaking the shotcrete. When a fault zone including such clay-rich gouge is pregrouted, washout of the gouge during tunnel excavation should be fully cared because the gouge itself is not cemented by pre-grouting due to its low-porosity.